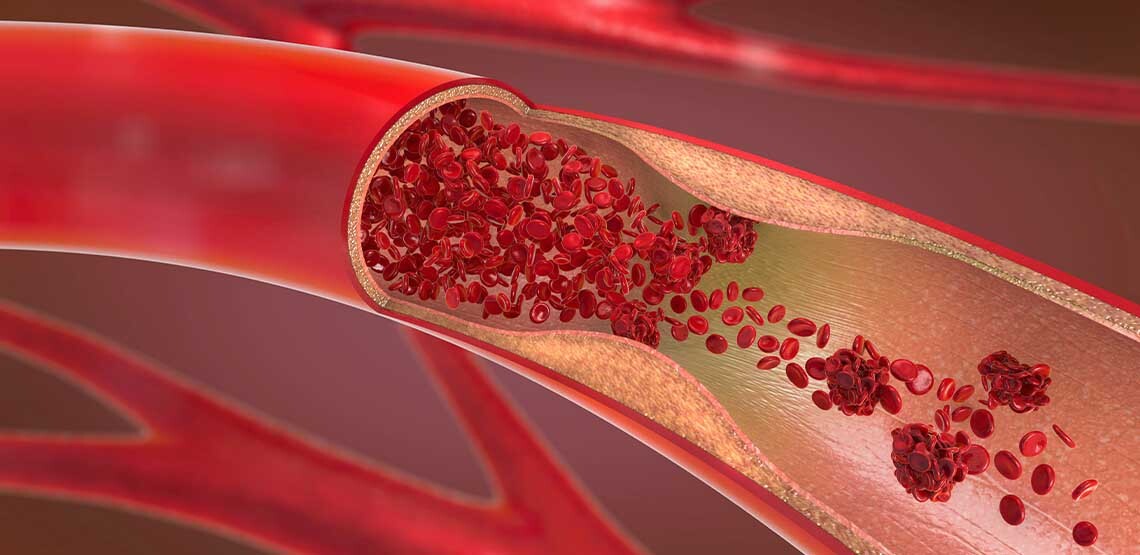
What Are the Signs of a Blood Clot?
In this article, we’ll examine all of this and more. A helpful treatment includes Eliquis (Apixaban); it is used to prevent serious blood clots from forming due to a certain irregular heartbeat (atrial fibrillation).
10 Signs and Symptoms of Blood Clots
Signs and symptoms tend to vary based on the location of the blood clot within the body.
A blood clot in the lower legs is very common. Symptoms of a blood clot in this area, other parts of the leg, or the arms, include:
- Pain.
- Tenderness.
- Swelling.
- Warmth.
- Redness.
If a blood clot happens in the heart, it will cause a heart attack. Symptoms may involve shortness of breath, chest pains, and light-headedness.
Related Search Topics (Ads)
When a blood clot happens in the brain, this is known as a stroke. You may have weakness on one side, difficulty speaking, and blurred vision. Knowing the signs of a stroke can help ensure the best outcome if this happens.
Meanwhile, a blood clot in the abdomen may mimic symptoms similar to the flu, food poisoning, or a stomach virus.
Lastly, a blood clot may occur in the lungs. This is called a pulmonary embolism. Symptoms may include:
- Shortness of breath.
- Chest pain.
- Issues breathing.
- Coughing up blood.
- A racing heart.
Understanding Blood Clots
A blood clot is essentially cells and proteins clumped together within your blood. It takes on a gel-like and semi-solid state. If it doesn’t dissolve when circulating, it can create various issues, including life-threatening situations.
A blood clot that stays in one spot, on the other hand, isn’t necessarily harmful. At least, not until it breaks free and travels through the body where it may eventually become stuck, creating a blockage in the heart or other areas.
Blood clots often form in the veins or arteries of the body. An arterial clot is when a blood clot forms in the arteries. This will often create immediate symptoms which require urgent medical attention. Meanwhile, a venous clot happens in the veins. These often gradually build over time, but it doesn’t make them any less life-threatening. Deep vein thrombosis is when a clot occurs in a major vein in the body. Usually, this happens in the legs. However, it may also occur in the lungs, brain, pelvis, arms, or legs.
Causes of Blood Clots
So, why might a blood clot form when there isn’t an injury? Usually, this is due to a combination of factors, such as:
- Prolonged bed rest or sitting (such as when someone is sick or when someone is sitting for long durations when traveling).
- Smoking.
- Obesity.
- Pregnancy.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT).
- A rare side effect of taking birth control pills.
- Cancer.
- Age.
- Autoimmune disorders.
- Chronic inflammatory diseases.
- Infections.
In other situations, a blood clot may form from a specific trigger, such as a traumatic injury or due to surgery complications.
Blood Clot Treatment
Complications with blood clots can arise since they increase your chances of having a heart attack or stroke, and possibly death. So, what can you do about it? How can you prevent the worst from happening?
Seeking proper treatment is of the utmost importance. From there, treatment will depend on the type of blood clot.
Your doctor may prescribe blood-thinning medications to prevent blood clots from forming or becoming a problem (such as getting bigger). Your doctor may also prescribe thrombolytic medications to break up any suspected blood clots within the body.
In some cases, you may require surgery to remove a venous clot in the arms or legs. However, the clot can be located elsewhere in the body. In other situations, your doctor may also recommend an intermittent pneumatic compression device. This device involves a cuff that is placed around the limb, such as your leg. This cuff fills with air at set intervals, which squeezes the area and helps move blood throughout the body.
Prevention
The good news is that blood clots are very much preventable. You can easily lower your risk by:
- Quitting smoking.
- Maintaining a healthy weight.
- Regular movement and exercise.
- Avoiding certain contraceptive methods that may increase your risk.
If your doctor is concerned, they may prescribe medication, such as a blood thinner, to also prevent blood clots from forming.
If you notice any symptoms of a blood clot, book a visit with your doctor. They can help you determine the best plan of action to prevent any future dangerous health incidents from happening. If you notice any life-threatening symptoms, such as those associated with a blood clot in the lungs, brain or heart, seek immediate medical attention.